Hepatobiliary Surgery
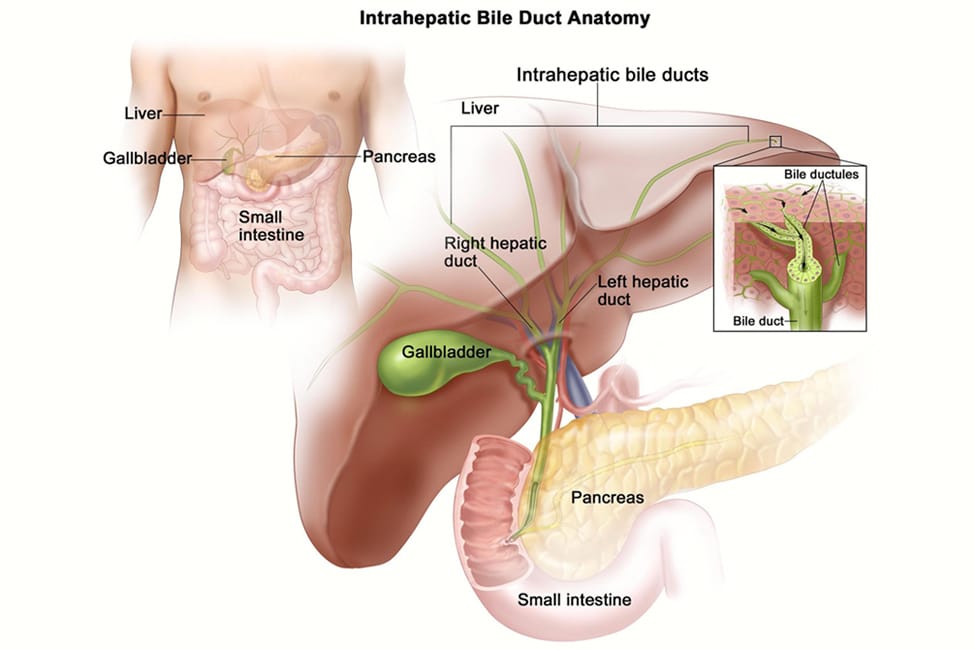
Hepatobiliary surgery is a subspecialty that surgically manages benign and malignant diseases of the liver and biliary tract. The biliary tract (also known as the biliary tree or biliary system) includes the liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts as they work together to produce, store, or deliver bile. Bile performs a critical function in our bodies as it aids in breaking down fat, the removal of bilirubin, the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, and more.
There are several reasons someone may require hepatobiliary surgery, including bile duct cancer, gallbladder cancer, and liver cancer. Surgery in this area can be complex and surgeons can use minimally invasive, laparoscopic surgeries to operate on the liver or biliary system. To treat these and other concerns affecting the biliary tract, surgeons perform precise, advanced surgeries such as resections of the liver, bile duct, or gallbladder.